cgitb – Detailed traceback reports¶
| Purpose: | cgitb provides more detailed traceback information than traceback. |
|---|---|
| Available In: | 2.2 and later |
cgitb was originally designed for showing errors and debugging information in web applications. It was later updated to include plain-text output as well, but unfortunately wasn’t renamed. This has led to obscurity and the module is not used as often as it should be. Nonetheless, cgitb is a valuable debugging tool in the standard library.
Standard Traceback Dumps¶
Python’s default exception handling behavior is to print a traceback to standard error with the call stack leading up to the error position. This basic output frequently contains enough information to understand the cause of the exception and permit a fix.
def func1(arg1):
local_var = arg1 * 2
return func2(local_var)
def func2(arg2):
local_var = arg2 + 2
return func3(local_var)
def func3(arg3):
local_var = arg2 / 2
return local_var
func1(1)
The above sample program has a subtle error in func3().
$ python cgitb_basic_traceback.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_basic_traceback.py", line 22, in <module>
func1(1)
File "cgitb_basic_traceback.py", line 12, in func1
return func2(local_var)
File "cgitb_basic_traceback.py", line 16, in func2
return func3(local_var)
File "cgitb_basic_traceback.py", line 19, in func3
local_var = arg2 / 2
NameError: global name 'arg2' is not defined
Enabling Detailed Tracebacks¶
While the basic traceback includes enough information for us to spot the error, enabling cgitb replaces sys.excepthook with a function that gives extended tracebacks with even more detail.
import cgitb
cgitb.enable(format='text')
def func1(arg1):
local_var = arg1 * 2
return func2(local_var)
def func2(arg2):
local_var = arg2 + 2
return func3(local_var)
def func3(arg3):
local_var = arg2 / 2
return local_var
func1(1)
As you can see below, the error report is much more extensive. Each frame of the stack is listed, along with:
- the full path to the source file, instead of just the base name
- the values of the arguments to each function in the stack
- a few lines of source context from around the line in the error path
- the values of variables in the expression causing the error
$ python cgitb_extended_traceback.py
<type 'exceptions.NameError'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:39 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_extended_traceback.py in <module>()
21 def func3(arg3):
22 local_var = arg2 / 2
23 return local_var
24
25 func1(1)
func1 = <function func1>
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_extended_traceback.py in func1(arg1=1)
13 def func1(arg1):
14 local_var = arg1 * 2
15 return func2(local_var)
16
17 def func2(arg2):
global func2 = <function func2>
local_var = 2
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_extended_traceback.py in func2(arg2=2)
17 def func2(arg2):
18 local_var = arg2 + 2
19 return func3(local_var)
20
21 def func3(arg3):
global func3 = <function func3>
local_var = 4
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_extended_traceback.py in func3(arg3=4)
20
21 def func3(arg3):
22 local_var = arg2 / 2
23 return local_var
24
local_var undefined
arg2 undefined
<type 'exceptions.NameError'>: global name 'arg2' is not defined
__class__ = <type 'exceptions.NameError'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__dict__ = {}
__doc__ = 'Name not found globally.'
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of exceptions.NameError object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__init__ = <method-wrapper '__init__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of exceptions.NameError object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of exceptions.NameError object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of exceptions.NameError object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of exceptions.NameError object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of exceptions.NameError object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of exceptions.NameError object>
args = ("global name 'arg2' is not defined",)
message = "global name 'arg2' is not defined"
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_extended_traceback.py", line 25, in <module>
func1(1)
File "cgitb_extended_traceback.py", line 15, in func1
return func2(local_var)
File "cgitb_extended_traceback.py", line 19, in func2
return func3(local_var)
File "cgitb_extended_traceback.py", line 22, in func3
local_var = arg2 / 2
NameError: global name 'arg2' is not defined
The end of the output also includes the full details of the exception object (in case it has attributes other than message that would be useful for debugging) and the original form of a traceback dump.
Local Variables in Tracebacks¶
Having access to the variables involved in the error stack can help find a logical error that occurs somewhere higher in the stack than the line where the actual exception is generated.
import cgitb
cgitb.enable(format='text')
def func2(a, divisor):
return a / divisor
def func1(a, b):
c = b - 5
return func2(a, c)
func1(1, 5)
In the case of this code with a ZeroDivisionError, we can see that the problem is introduced in the computation of the value of c in func1(), rather than where the value is used in func2().
$ python cgitb_local_vars.py
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:39 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_local_vars.py in <module>()
16 def func1(a, b):
17 c = b - 5
18 return func2(a, c)
19
20 func1(1, 5)
func1 = <function func1>
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_local_vars.py in func1(a=1, b=5)
16 def func1(a, b):
17 c = b - 5
18 return func2(a, c)
19
20 func1(1, 5)
global func2 = <function func2>
a = 1
c = 0
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_local_vars.py in func2(a=1, divisor=0)
12
13 def func2(a, divisor):
14 return a / divisor
15
16 def func1(a, b):
a = 1
divisor = 0
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>: integer division or modulo by zero
__class__ = <type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__dict__ = {}
__doc__ = 'Second argument to a division or modulo operation was zero.'
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__init__ = <method-wrapper '__init__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
args = ('integer division or modulo by zero',)
message = 'integer division or modulo by zero'
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_local_vars.py", line 20, in <module>
func1(1, 5)
File "cgitb_local_vars.py", line 18, in func1
return func2(a, c)
File "cgitb_local_vars.py", line 14, in func2
return a / divisor
ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
The code in cgitb that examines the variables used in the stack frame leading to the error is smart enough to evaluate object attributes to display them, too.
import cgitb
cgitb.enable(format='text')
class BrokenClass(object):
"""This class has an error.
"""
def __init__(self, a, b):
"""Be careful passing arguments in here.
"""
self.a = a
self.b = b
self.c = self.a * self.b
self.d = self.a / self.b
return
o = BrokenClass(1, 0)
Here we see that self.a and self.b are involved in the error-prone code.
$ python cgitb_with_classes.py
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:39 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_with_classes.py in <module>()
24 return
25
26 o = BrokenClass(1, 0)
27
28
o undefined
BrokenClass = <class '__main__.BrokenClass'>
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_with_classes.py in __init__(self=<__main__.BrokenClass object>, a=1, b=0)
21 self.b = b
22 self.c = self.a * self.b
23 self.d = self.a / self.b
24 return
25
self = <__main__.BrokenClass object>
self.d undefined
self.a = 1
self.b = 0
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>: integer division or modulo by zero
__class__ = <type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__dict__ = {}
__doc__ = 'Second argument to a division or modulo operation was zero.'
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__init__ = <method-wrapper '__init__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
args = ('integer division or modulo by zero',)
message = 'integer division or modulo by zero'
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_with_classes.py", line 26, in <module>
o = BrokenClass(1, 0)
File "cgitb_with_classes.py", line 23, in __init__
self.d = self.a / self.b
ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
Adding More Context¶
Suppose your function includes a lot of inline comments, whitespace, or other code that makes it very long. Having the default of 5 lines of context may not be enough help in that case, if the body of the function is pushed out of the code window displayed. Using a larger context value when enabling cgitb gets around this.
import cgitb
import sys
context_length = int(sys.argv[1])
cgitb.enable(format='text', context=context_length)
def func2(a, divisor):
return a / divisor
def func1(a, b):
c = b - 5
# Really
# long
# comment
# goes
# here.
return func2(a, c)
func1(1, 5)
You can pass context to enable() to control the amount of code displayed for each line of the traceback.
$ python cgitb_more_context.py 5
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:39 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_more_context.py in <module>()
24 # goes
25 # here.
26 return func2(a, c)
27
28 func1(1, 5)
func1 = <function func1>
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_more_context.py in func1(a=1, b=5)
24 # goes
25 # here.
26 return func2(a, c)
27
28 func1(1, 5)
global func2 = <function func2>
a = 1
c = 0
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_more_context.py in func2(a=1, divisor=0)
15
16 def func2(a, divisor):
17 return a / divisor
18
19 def func1(a, b):
a = 1
divisor = 0
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>: integer division or modulo by zero
__class__ = <type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__dict__ = {}
__doc__ = 'Second argument to a division or modulo operation was zero.'
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__init__ = <method-wrapper '__init__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
args = ('integer division or modulo by zero',)
message = 'integer division or modulo by zero'
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_more_context.py", line 28, in <module>
func1(1, 5)
File "cgitb_more_context.py", line 26, in func1
return func2(a, c)
File "cgitb_more_context.py", line 17, in func2
return a / divisor
ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
Increasing the value gets us enough of the function that we can spot the problem in the code, again.
$ python cgitb_more_context.py 10
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:39 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_more_context.py in <module>()
19 def func1(a, b):
20 c = b - 5
21 # Really
22 # long
23 # comment
24 # goes
25 # here.
26 return func2(a, c)
27
28 func1(1, 5)
func1 = <function func1>
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_more_context.py in func1(a=1, b=5)
19 def func1(a, b):
20 c = b - 5
21 # Really
22 # long
23 # comment
24 # goes
25 # here.
26 return func2(a, c)
27
28 func1(1, 5)
global func2 = <function func2>
a = 1
c = 0
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_more_context.py in func2(a=1, divisor=0)
12
13 context_length = int(sys.argv[1])
14 cgitb.enable(format='text', context=context_length)
15
16 def func2(a, divisor):
17 return a / divisor
18
19 def func1(a, b):
20 c = b - 5
21 # Really
a = 1
divisor = 0
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>: integer division or modulo by zero
__class__ = <type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__dict__ = {}
__doc__ = 'Second argument to a division or modulo operation was zero.'
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__init__ = <method-wrapper '__init__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
args = ('integer division or modulo by zero',)
message = 'integer division or modulo by zero'
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_more_context.py", line 28, in <module>
func1(1, 5)
File "cgitb_more_context.py", line 26, in func1
return func2(a, c)
File "cgitb_more_context.py", line 17, in func2
return a / divisor
ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
Exception Properties¶
In addition to the local variables from each stack frame, cgitb shows all properties of the exception object. If you have a custom exception type with extra properties, they are printed as part of the error report.
import cgitb
cgitb.enable(format='text')
class MyException(Exception):
"""Add extra properties to a special exception
"""
def __init__(self, message, bad_value):
self.bad_value = bad_value
Exception.__init__(self, message)
return
raise MyException('Normal message', bad_value=99)
In this example, the bad_value property is included along with the standard message and args values.
$ python cgitb_exception_properties.py
<class '__main__.MyException'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:39 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_exception_properties.py in <module>()
18 self.bad_value = bad_value
19 Exception.__init__(self, message)
20 return
21
22 raise MyException('Normal message', bad_value=99)
MyException = <class '__main__.MyException'>
bad_value undefined
<class '__main__.MyException'>: Normal message
__class__ = <class '__main__.MyException'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of MyException object>
__dict__ = {'bad_value': 99}
__doc__ = 'Add extra properties to a special exception\n '
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of MyException object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of MyException object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of MyException object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of MyException object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of MyException object>
__init__ = <bound method MyException.__init__ of MyException('Normal message',)>
__module__ = '__main__'
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of MyException object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of MyException object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of MyException object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of MyException object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of MyException object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of MyException object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of MyException object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of MyException object>
__weakref__ = None
args = ('Normal message',)
bad_value = 99
message = 'Normal message'
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_exception_properties.py", line 22, in <module>
raise MyException('Normal message', bad_value=99)
MyException: Normal message
Logging Tracebacks¶
For many situations, printing the traceback details to standard error is the best resolution. In a production system, however, logging the errors is even better. enable() includes an optional argument, logdir, to enable error logging. When a directory name is provided, each exception is logged to its own file in the given directory.
import cgitb
import os
cgitb.enable(logdir=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'LOGS'),
display=False,
format='text',
)
def func2(a, divisor):
return a / divisor
def func1(a, b):
c = b - 5
return func2(a, c)
func1(1, 5)
Even though the error display is suppressed, a message is printed describing where to go to find the error log.
$ python cgitb_log_exception.py
<p>A problem occurred in a Python script.
<p> /Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/LOGS/tmpju23ip.txt contains the description of this error.
$ ls LOGS
tmpju23ip.txt
$ cat LOGS/*.txt
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
Python 2.7.2: /Users/dhellmann/Envs/pymotw/bin/python
Thu Feb 21 06:35:40 2013
A problem occurred in a Python script. Here is the sequence of
function calls leading up to the error, in the order they occurred.
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_log_exception.py in <module>()
21 def func1(a, b):
22 c = b - 5
23 return func2(a, c)
24
25 func1(1, 5)
func1 = <function func1>
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_log_exception.py in func1(a=1, b=5)
21 def func1(a, b):
22 c = b - 5
23 return func2(a, c)
24
25 func1(1, 5)
global func2 = <function func2>
a = 1
c = 0
/Users/dhellmann/Documents/PyMOTW/src/PyMOTW/cgitb/cgitb_log_exception.py in func2(a=1, divisor=0)
17
18 def func2(a, divisor):
19 return a / divisor
20
21 def func1(a, b):
a = 1
divisor = 0
<type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>: integer division or modulo by zero
__class__ = <type 'exceptions.ZeroDivisionError'>
__delattr__ = <method-wrapper '__delattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__dict__ = {}
__doc__ = 'Second argument to a division or modulo operation was zero.'
__format__ = <built-in method __format__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getattribute__ = <method-wrapper '__getattribute__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getitem__ = <method-wrapper '__getitem__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__getslice__ = <method-wrapper '__getslice__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__hash__ = <method-wrapper '__hash__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__init__ = <method-wrapper '__init__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__new__ = <built-in method __new__ of type object>
__reduce__ = <built-in method __reduce__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__reduce_ex__ = <built-in method __reduce_ex__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__repr__ = <method-wrapper '__repr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setattr__ = <method-wrapper '__setattr__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__setstate__ = <built-in method __setstate__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__sizeof__ = <built-in method __sizeof__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__str__ = <method-wrapper '__str__' of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
__subclasshook__ = <built-in method __subclasshook__ of type object>
__unicode__ = <built-in method __unicode__ of exceptions.ZeroDivisionError object>
args = ('integer division or modulo by zero',)
message = 'integer division or modulo by zero'
The above is a description of an error in a Python program. Here is
the original traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "cgitb_log_exception.py", line 25, in <module>
func1(1, 5)
File "cgitb_log_exception.py", line 23, in func1
return func2(a, c)
File "cgitb_log_exception.py", line 19, in func2
return a / divisor
ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
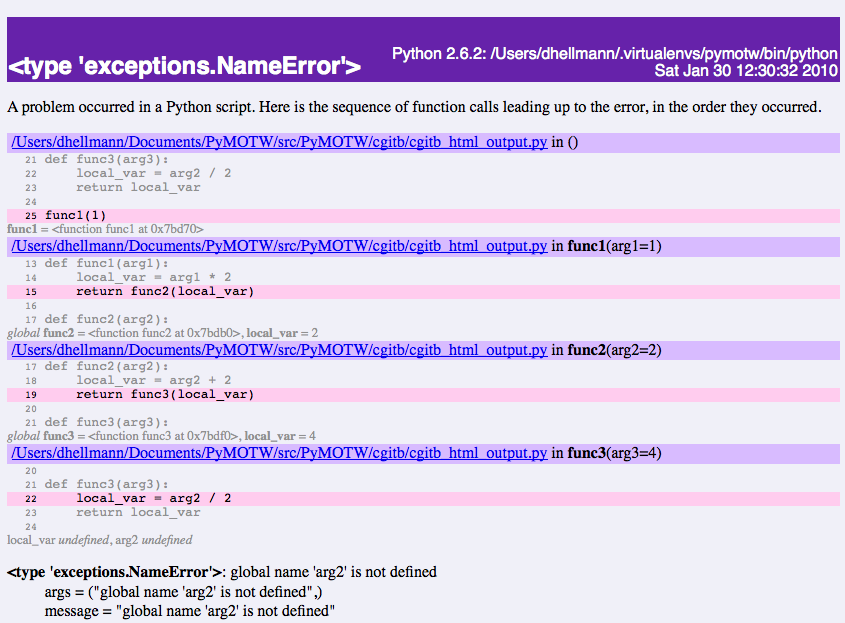
HTML Output¶
Because cgitb was originally developed for handling exceptions in web apps, no discussion would be complete without an example of the HTML output it produces.
import cgitb
cgitb.enable()
def func1(arg1):
local_var = arg1 * 2
return func2(local_var)
def func2(arg2):
local_var = arg2 + 2
return func3(local_var)
def func3(arg3):
local_var = arg2 / 2
return local_var
func1(1)
By leaving out the format argument (or specifying html), the traceback format changes to HTML output.
See also
- cgitb
- The standard library documentation for this module.
- traceback
- Standard library module for working with tracebacks.
- inspect
- The inspect module includes more functions for examining the stack.
- sys
- The sys module provides access to the current exception value and the excepthook handler invoked when an exception occurs.
- Improved traceback module
- Python-dev discussion of improvements to the traceback module and related enhancements other developers use locally.

